📝문제 설명

📢입출력 예시
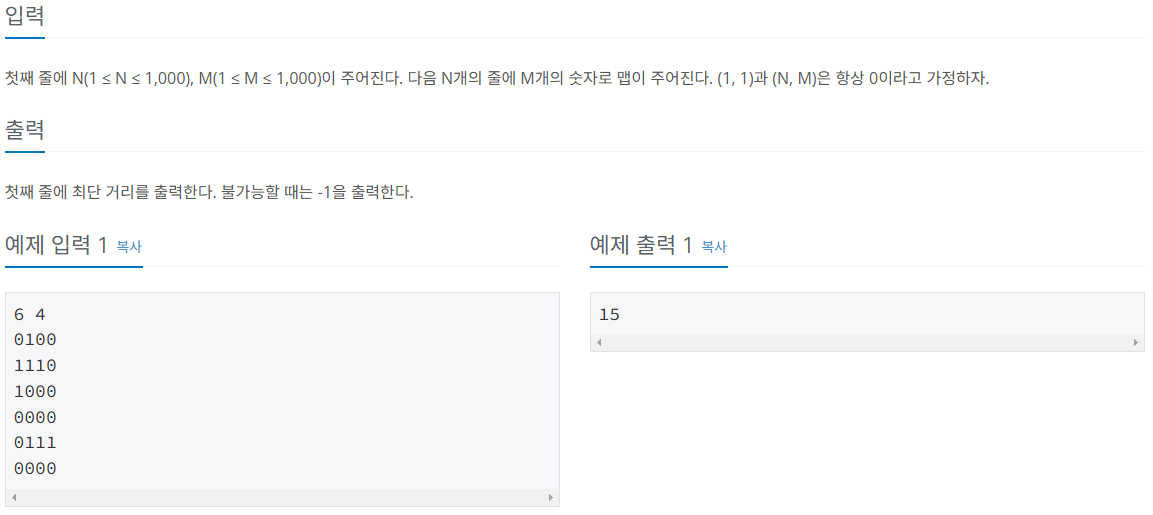
✏️문제 풀이
정답 코드
package Baekjoon.Graph;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Baek2206_1 {
static int N, M;
static int[][] map;
static boolean[][][] visited;
static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[N][M];
visited = new boolean[N][M][2]; // [x][y][0]: 벽 안 부숨, [x][y][1]: 벽 부숨
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
String string = bf.readLine();
for(int j=0; j<M; j++){
map[i][j] = string.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
int result = BFS();
System.out.println(result);
}
private static int BFS(){
Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Point(0,0,1,0));
visited[0][0][0] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Point point = queue.poll();
int currentX = point.x;
int currentY = point.y;
int currentDis = point.dis;
int currentStatus = point.wallBroken;
if(currentX == N-1 && currentY == M-1){
return currentDis;
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int newX = currentX + dx[i];
int newY = currentY + dy[i];
if (newX >= 0 && newY >= 0 && newX < N && newY < M) {
// 안부순 상태로 이동
if (map[newX][newY] == 0 && !visited[newX][newY][currentStatus]) {
queue.offer(new Point(newX, newY, currentDis + 1, currentStatus));
visited[newX][newY][currentStatus] = true;
}
// 부수고 이동
if(map[newX][newY] == 1 && !visited[newX][newY][1] && currentStatus == 0){
queue.offer(new Point(newX, newY, currentDis+1, 1));
visited[newX][newY][1] = true;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private static class Point{
int x;
int y;
int dis;
int wallBroken;
Point(int x, int y, int dis, int wallBroken){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.dis = dis;
this.wallBroken = wallBroken;
}
}
}- DFS에서 백트래킹 방식으로 모든 좌표의 벽을 부수면서 BFS를 호출하여 최단 거리를 측정하면 시간초과가 발생
- 벽을 부순 상태와 부수지 않은 상태를 분리하여 관리하기 위해 visited 배열을 3차원으로 관리
- vistied[x][y][k]
k = 0 : 벽을 부수지 않고 방문한 상태
k = 1 : 벽을 부수고 방문한 상태
if (map[newX][newY] == 0 && !visited[newX][newY][currentStatus]) {
queue.offer(new Point(newX, newY, currentDis + 1, currentStatus));
visited[newX][newY][currentStatus] = true;
}다음 이동 경로가 벽이 아니고, 방문하지 않은 상태라면 큐에 추가하고 방문 표시를 한다.
if(map[newX][newY] == 1 && !visited[newX][newY][1] && currentStatus == 0){
queue.offer(new Point(newX, newY, currentDis+1, 1));
visited[newX][newY][1] = true;
}다음 이동 경로가 벽이고, 아직 벽을 부수지 않은 상태라면 벽 부수고 이동한다.
틀린 코드
package Baekjoon.Graph;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Baek2206 {
static int N,M;
static int[][] map, copymap;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
static int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[N][M];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
String string = bf.readLine();
for(int j=0; j<M; j++){
map[i][j] = string.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
DFS(0);
System.out.println(min);
}
private static void DFS(int depth){
if(depth == 1){
int result = BFS();
Cal(result);
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
for(int j=0; j<M; j++){
if(map[i][j] == 1){
map[i][j] = 0;
DFS(depth+1);
map[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
private static int BFS(){
visited = new boolean[N][M];
Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Point(0,0,1));
visited[0][0] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Point point = queue.poll();
int currentX = point.x;
int currentY = point.y;
int currentDis = point.dis;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
int newX = currentX + dx[i];
int newY = currentY + dy[i];
if(newX == N-1 && newY == M-1){
return currentDis+1;
}
if(newX >= 0 && newY >= 0 && newX <N && newY <M){
if(map[newX][newY] == 0 && !visited[newX][newY]){
queue.offer(new Point(newX,newY,currentDis+1));
visited[newX][newY] = true;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private static void Cal(int result){
if(result != -1) {
min = Math.min(result, min);
}else{
min = -1;
}
}
private static class Point{
int x;
int y;
int dis;
Point(int x, int y, int dis){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.dis = dis;
}
}
}💡새로 알게된 점
https://dongyeop00.tistory.com/164
JAVA [Algorithm] - 백준 14502 연구소
📝문제 설명 - 0은 빈칸, 1은 벽, 2는 바이러스- 바이러스는 상하좌우로 움직이며 벽으로 가로막혀 있으면 퍼질 수 없다.- 벽을 3개를 모두 세운 뒤 바이러스를 퍼트린 후, 0 빈칸의 개수가 최대인
dongyeop00.tistory.com
map에서 어떠한 동작을 수행 후 bfs를 수행한다는 것을 보고 dfs와 bfs를 혼합한 연구소 문제와 비슷하다고 생각하여
틀린 코드처럼 dfs에서 벽을 부순 후 bfs를 수행하여 최단 거리를 구했다.

하지만 시간 초과가 뜨는 걸 보니 시간 초과가 왜 뜨는지 계산 해보았다.
- 틀린 코드 시간 복잡도
1. BFS 탐색 방식
- N x M에 대해 모든 노드를 탐색 -> O(n*m)
2. DFS 호출 회수
- 벽의 개수를 기준으로 탐색하며, 각 경우 마다 BFS 호출 -> O(n*m)
3. 총 시간 복잡도
O( (n*m) * (n*m) ) = O(n^2 * m^2)
4. 맵 크기 제한
N, M <= 1000
- O(1000^2 * 1000^2) = 10^12
5. 결과
시간 제한은 2초이고 10^12는 2초보다 크므로 BFS에서 해결 방법을 생각했어야 했다.
- 연구소 문제와 차이점
시간 복잡도를 계산하기 전에는 비슷한 유형처럼 보이는 문제이다. 그렇다면 시간 복잡도를 떠나 둘의 차이점과 접근 방향은 어떻게 잡아야 할까?
1. 연구소 문제
- "벽을 어디에 설치할 것인가"의 조합 문제
- 가능한 모든 벽 설치 위치를 탐색해야 하므로 DFS를 사용
2. 벽 부수고 이동하기 문제
- "모든 경우의 수를 탐색"하는 DFS보다는 "최단 거리"를 먼저 찾는 BFS 문제
3. 핵심 차이
- 연구소 문제 : 조합을 탐색하여 최적의 경우를 찾는다.
- 벽 부수고 이동하기 문제 : 여러 상태를 고려하며 최단 경로를 찾는다.
'📖Algorithm > DFS & BFS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JAVA [Algorithm] - 백준 14502 연구소 (0) | 2024.12.18 |
|---|---|
| JAVA [Algorithm] - 백준 7576 토마토 (1) | 2024.12.17 |
| JAVA [Algorithm] - 백준 1697 숨바꼭질 (0) | 2024.12.16 |
| JAVA [Algorithm] - 백준 2178 미로 탐색 (2) | 2024.12.14 |
| JAVA [Algorithm] - 백준 2667 단지번호 붙이기 (0) | 2024.12.14 |

